Understanding EV Urban Networks and Their Role in Green Mobility
Electric Vehicle (EV) urban networks are more than just charging stations. They represent a new layer of smart city infrastructure—one that connects mobility, sustainability, and technology. As cities seek to reduce carbon emissions and ease traffic congestion, EV networks are proving to be crucial components of this transformation.
From Isolated Chargers to Integrated Systems
In the early stages, EV chargers were often standalone units in parking lots. Today, they’re evolving into data-rich, connected nodes integrated with public transit, parking systems, and renewable energy grids. This integration not only enhances user convenience but also supports better energy management.
Why Urban EV Infrastructure Matters
Urban centers are home to dense populations and frequent traffic. Therefore, effective EV urban networks reduce reliance on fossil fuels, improve air quality, and create smoother, smarter transportation ecosystems. Additionally, accessible charging points encourage adoption of EVs across all income levels.
Smart City Synergy: How Charging Networks Fit the Urban Puzzle
Smart cities depend on interconnected infrastructure. EV charging stations are ideal touchpoints for merging transportation, energy, and data systems into a cohesive whole.
Real-Time Data and Predictive Analytics
Modern EV networks use real-time data to optimize energy distribution and minimize grid stress during peak hours. With predictive analytics, cities can plan future installations based on usage patterns and demand forecasts.
EV Urban Networks and Renewable Energy
Many networks now pair with solar panels or wind turbines, enabling clean energy loops. This approach not only supports green mobility but also decreases overall energy costs in the long run.
Challenges and Opportunities in EV Urban Expansion
Despite the benefits, deploying effective EV urban networks presents logistical and financial hurdles. However, smart planning and public-private collaboration can overcome them.
Infrastructure Gaps in Developing Cities
Emerging economies often lack the foundational infrastructure for EV growth. Yet, by integrating charging networks into new urban developments, these cities can leapfrog older systems and go directly to smart, sustainable models.
Policy, Regulation, and Public Incentives
Supportive government policies are essential. From tax rebates to zoning support, incentives help accelerate adoption and ensure EV networks expand equitably across urban areas.
Shaping the Future: What Comes Next for EV Urban Networks?
As cities continue to digitize, EV infrastructure will evolve in tandem. Future developments will include autonomous charging, AI-powered routing, and integration with digital twins of city environments.
Connected Mobility Ecosystems
Eventually, EV charging won’t be a separate service—it will be part of a wider connected mobility platform. These systems will sync with traffic signals, public transport schedules, and smart parking, making mobility seamless and sustainable.
Beyond Cars: Expanding to E-Bikes and Public Fleets
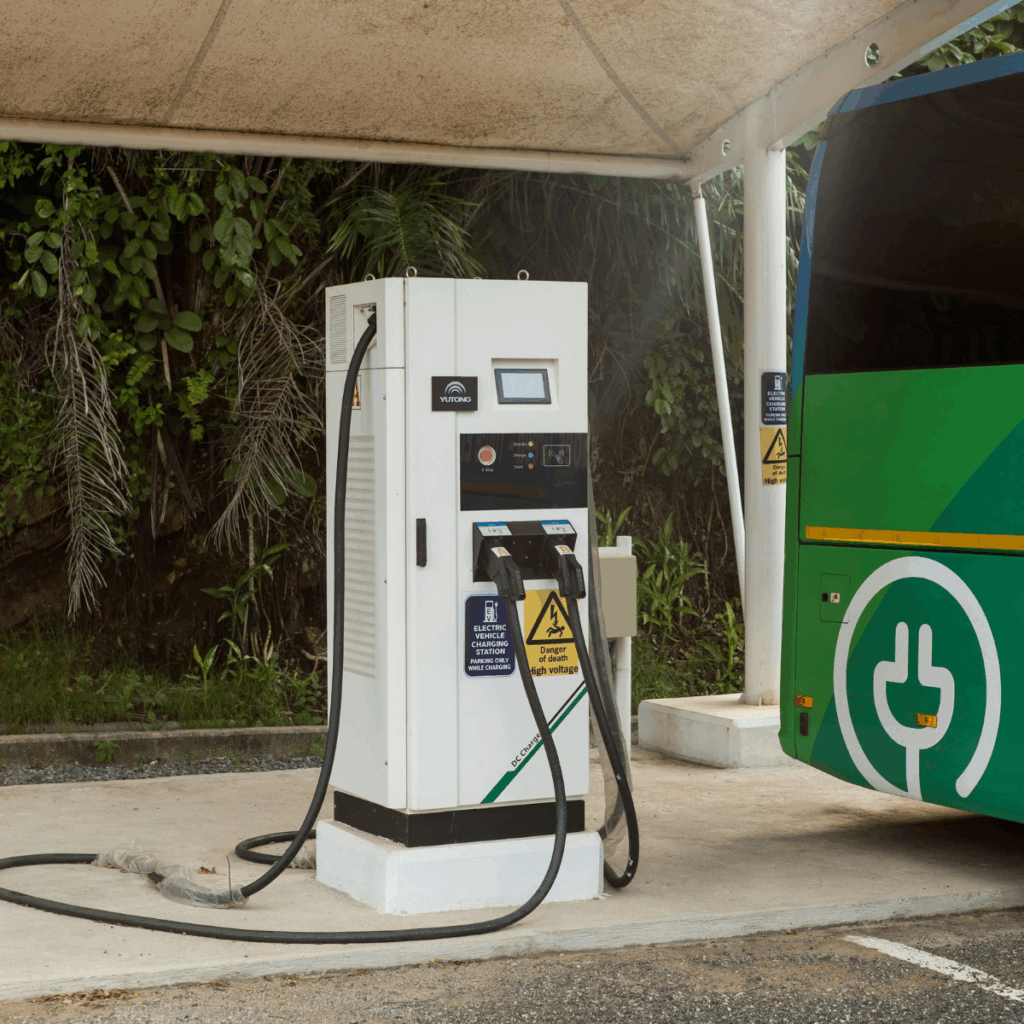
To truly embrace green mobility, cities must think beyond personal EVs. Charging infrastructure for electric buses, delivery vans, and e-bikes is essential for broader environmental impact.
Conclusion
EV urban networks are at the heart of sustainable urban transformation. By linking clean energy, real-time data, and connected infrastructure, these systems are enabling cities to reduce emissions and prepare for a more resilient future. Their success, however, hinges on collaboration—between governments, private sectors, and communities—to ensure that green mobility is accessible, scalable, and smart.Explore how MTi Arabia can help you leverage these trends to revolutionize your city. Contact us here.