Introduction
Smart cities are becoming essential in the quest for sustainable urban development. As global populations grow and environmental concerns increase, integrating green technology and renewable energy into urban infrastructure is no longer an option—it’s a necessity. The concept of green smart cities combines cutting-edge technology with environmentally conscious solutions to create efficient, sustainable, and livable urban spaces. This article explores how green technology and renewable energy are driving the future of smart cities and why they are crucial for long-term urban success.
What Are Green Smart Cities?
Green smart cities are urban areas that use technology and renewable energy to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance the quality of life for residents. These cities integrate digital infrastructure, smart grids, and eco-friendly solutions to create a balanced, sustainable urban ecosystem.
Key components of green smart cities include:
- Renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro)
- Smart grids and energy-efficient systems
- Sustainable transportation (electric vehicles, smart public transport)
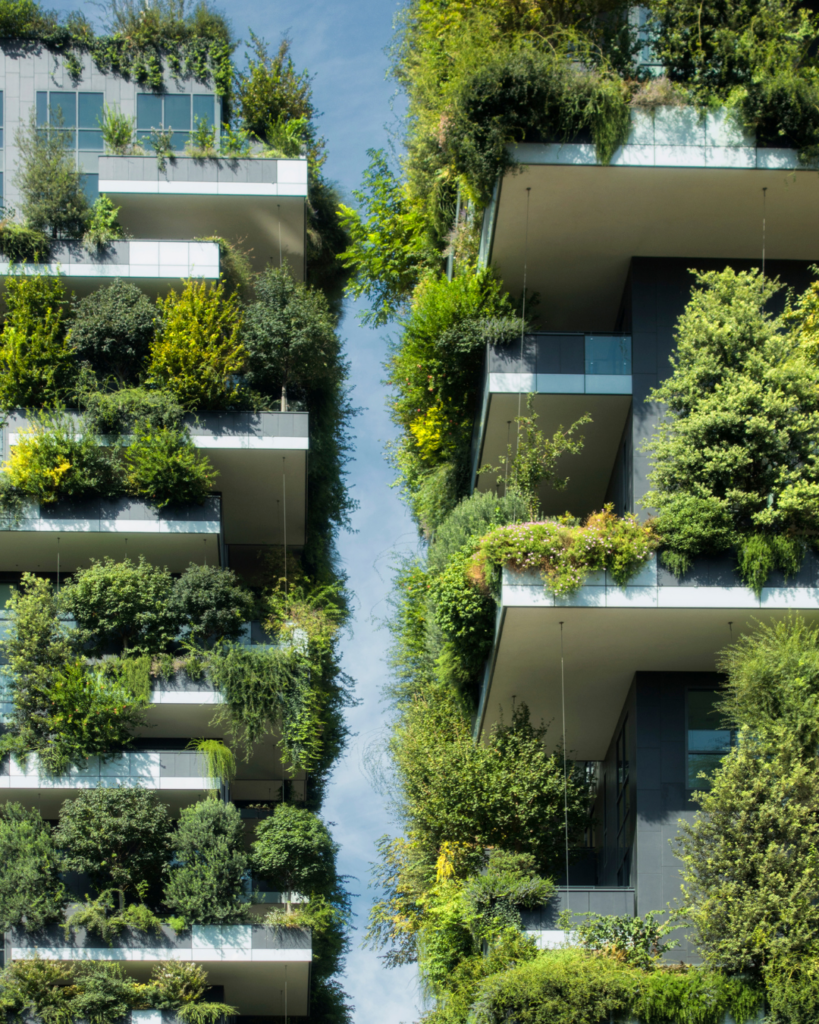
- Green architecture and eco-friendly building materials
- Waste reduction and recycling programs
Why Green Smart Cities Matter
Urban areas are responsible for over 70% of global carbon emissions. With rapid urbanization, the pressure on resources and infrastructure continues to grow. Smart cities address these challenges by reducing energy consumption, cutting emissions, and promoting sustainable growth.
Transitioning to green smart cities is not just about environmental impact—it also drives economic benefits by reducing operational costs, improving infrastructure resilience, and creating new job opportunities in the green technology sector.
Key Technologies Driving Green Smart Cities
1. Renewable Energy Integration
One of the fundamental elements of Smart Cities is the shift toward renewable energy. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power reduce dependency on fossil fuels and cut overall carbon emissions.
- Solar Energy: Smart cities are increasingly installing solar panels on public buildings, streetlights, and residential homes to harness solar energy .
- Wind Energy: Offshore and onshore wind farms supply sustainable energy to the grid.
- Hydroelectric Power: Smart water management systems help harness energy from water flow in urban environments.
2. Smart Grids and Energy Management
Smart grids play a critical role in balancing energy supply and demand. These systems use real-time data and artificial intelligence (AI) to distribute energy efficiently, reducing waste and lowering costs.
- Smart meters and sensors monitor energy use and provide insights for better management.
- AI-driven systems predict energy demand and adjust supply accordingly.
- Integration with renewable sources ensures a stable and consistent power supply.
3. Sustainable Transportation Solutions
Transportation is a major contributor to urban emissions. Smart cities focus on reducing this impact through smart mobility solutions:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Charging stations and EV-friendly infrastructure encourage cleaner transportation.
- Smart Public Transport: AI-driven systems optimize routes and schedules to reduce congestion and emissions.
- Bike-sharing and Pedestrian Zones: Cities promote walkability and reduce car dependence.
Challenges and Opportunities in Developing Green Smart Cities
Infrastructure and Investment
Developing smart cities requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology. Governments and private sectors must work together to finance and implement smart city projects.
- Investment in smart grids and renewable energy facilities
- Partnerships with tech companies for AI and IoT solutions
- Incentives for citizens to adopt green practices
Data Security and Privacy
Smart cities rely on data from sensors and connected devices. Protecting this data is essential to maintaining public trust and operational security.
- Strong cybersecurity protocols
- Transparent data collection policies
- Regular audits and system updates
Public Engagement and Education
Public support is critical to the success of smart cities. Educating residents about the benefits of smart technologies and encouraging participation in sustainable initiatives helps create a more engaged and eco-conscious community.
The Future of Green Smart Cities
As technology advances, smart cities will continue to evolve. Innovations in AI, machine learning, and IoT will enable more efficient energy management, improved mobility solutions, and enhanced environmental monitoring.
Cities like Singapore, Copenhagen, and Amsterdam are already demonstrating the potential of smart cities. Saudi Arabia’s NEOM project is another example of a large-scale smart city initiative focused on sustainability and innovation.
Green smart cities are not just a vision—they are becoming a reality. By embracing renewable energy and smart technologies, cities can reduce environmental impact, improve quality of life, and ensure long-term resilience.
Conclusion
Building smart cities with green technology and renewable energy is essential for creating sustainable and resilient urban spaces. Green smart cities not only address environmental challenges but also unlock economic and social benefits. By investing in renewable energy, smart grids, and sustainable transport, cities can pave the way for a smarter, greener future.Discover how MTi Arabia can help you implement the latest innovations in your industry. Get in touch with our experts today. Contact us here.